MOLD TOOL
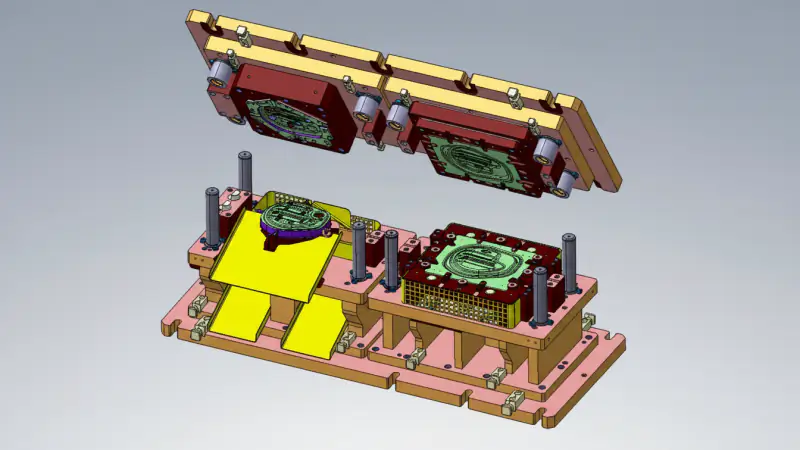
Mold Tool
Introduction to Mold Tools
Mold tools play a critical in manufacturing, particularly in industries that require the mass production of precise and complex parts. From automotive to electronics, mold tools ensure the efficient production of high-quality products across multiple sectors. In this blog article, we will delve into the technicalities, functionality, applications, and future trends in mold tool technology. With decades of experience in various customer projects, we at Evomatec guarantee that our inspections are always carried out with the highest level of care regarding quality and CE-compliant safety standards.
What is a Mold Tool?
A mold tool is a machine or system used to shape materials into specific forms through molding processes. These tools are commonly used in industries such as plastics, aluminum, and metalworking, where precision and repeatability are essential. Mold tools are typically made from high-strength materials to withstand the pressure and temperatures of the molding process.
Types of Mold Tools
Injection Molding Tools
Functionality: Injection molding tools are used to inject molten materials, such as plastic or metal, into a mold to form a specific shape. These tools are widely used in the production of plastic components in automotive, consumer goods, and electronics industries.
Applications: Manufacturing plastic parts, automotive components, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
Compression Molding Tools
Functionality: Compression molding involves placing a material into an open mold cavity, which is then closed and compressed to shape the material. These tools are used for materials like rubber and thermosets.
Applications: Rubber parts, thermoset components, and automotive sealing systems.
Die-Cutting Tools
Functionality: Die-cutting tools are used to cut materials into specific shapes and sizes, often used in packaging and textile industries.
Applications: Packaging, automotive gaskets, textile materials.
Extrusion Molding Tools
Functionality: In extrusion molding, the material is forced through a mold to create long shapes like pipes or sheets. These tools are highly effective for continuous production.
Applications: PVC profiles, aluminum extrusion, food packaging materials.
Technical Aspects of Mold Tools
Material Selection
Mold tools are often made from hardened steels or carbide, which provide the strength required to withstand the high pressures and temperatures typical of molding processes. The material choice depends on the type of molding process and the material being molded.
Precision and Tolerances
One of the most critical aspects of mold tools is precision. The molds must be manufactured to very tight tolerances to ensure that the parts produced meet the required specifications. A deviation in mold design can result in defects such as misalignment, poor surface finish, or dimensional inaccuracies.
Cooling Systems
Cooling systems integrated into mold tools are essential to ensure that the molded material solidifies at the correct rate. Inefficient cooling can lead to warping, dimensional changes, or defects in the part. Many modern mold tools feature advanced cooling technologies that enhance the overall efficiency of the molding process.
Automation and Control Systems
Modern mold tools are equipped with sophisticated control systems that allow for automated operation, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing production efficiency. These tools are often integrated with robotic systems to automate loading and unloading processes, ensuring consistent part quality and minimizing production time.
Applications of Mold Tools
Automotive Industry
Mold tools are extensively used in the automotive industry to produce components such as dashboards, door panels, bumpers, and more. These components require precise manufacturing to meet safety and design standards.
Consumer Electronics
The production of consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, relies heavily on mold tools for components like casings, buttons, and connectors. Precision is essential to ensure the functionality and aesthetics of the final product.
Packaging Industry
Mold tools are used in the creation of packaging materials, including containers, bottles, and trays. In this industry, high-speed production and cost efficiency are key factors driving the use of advanced mold tools.
Medical Devices
Mold tools are essential in the production of medical devices, which require the highest level of accuracy and consistency. Components such as syringes, surgical instruments, and prosthetics are often molded using specialized tools.
Advantages of Using Mold Tools
High Efficiency
Mold tools enable mass production of identical parts with minimal waste, making them highly efficient for industries that require high volumes of components.
Precision and Consistency
Mold tools ensure that parts are manufactured with high precision and uniformity, ensuring that each part meets the required specifications.
Cost-Effective
While the initial investment in mold tools can be high, the long-term benefits of mass production and reduced labor costs make them a cost-effective solution for many industries.
Versatility
Mold tools can be used for a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites, allowing manufacturers to create components for diverse industries.
Challenges in Mold Tool Manufacturing
Initial Setup Costs
The cost of designing and manufacturing mold tools can be significant, especially for complex molds. However, this cost is often offset by the high-volume production capabilities.
Tool Wear and Maintenance
Over time, mold tools can experience wear, which can affect the quality of the parts produced. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn parts are essential to maintain optimal performance.
Design Complexity
Designing molds for intricate parts requires advanced expertise in both engineering and material science. Complex parts may require the development of custom mold tools, which can increase both time and cost.
The Future of Mold Tools
The future of mold tools is closely linked to advancements in technology, particularly in the areas of automation, robotics, and 3D printing. 3D printing technologies, for instance, are beginning to play a in mold manufacturing, offering the potential for faster prototyping and the creation of complex, custom molds with less material waste.
Additionally, as industries continue to push for more sustainable and eco-friendly production methods, mold tools will evolve to accommodate new, environmentally friendly materials. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into mold tool design and operation will also enhance process efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve product quality.
Conclusion
Mold tools are essential to modern manufacturing, enabling the mass production of high-quality, precision parts across a variety of industries. By leveraging advancements in material science, automation, and digital technologies, mold tools will continue to evolve, driving greater efficiency and innovation in manufacturing processes.
FAQ
What is the difference between injection molding and compression molding?
Injection molding involves injecting molten material into a mold under pressure, while compression molding involves placing material into an open mold and closing it to shape. Injection molding is typically faster and suitable for more complex parts.
How do mold tools ensure part accuracy?
Mold tools are designed to extremely tight tolerances, often to within microns, ensuring that parts are produced consistently with high precision. Advanced control systems and quality checks are integrated to maintain this accuracy throughout production.
Can mold tools be used for both metals and plastics?
Yes, mold tools can be used for both metals and plastics, depending on the process and material being used. For instance, die-casting is used for metals, while injection molding is used for plastics.
Contac us: info@evomatec.de

 English
English
 German
German
 French
French
 Spanish
Spanish
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Italian
Italian
 Polish
Polish
 Turkish
Turkish
 Romanian
Romanian
 Greek
Greek
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian
 Russian
Russian
 Arabic
Arabic
 Hindi
Hindi